本文的主要目标:1.介绍3D Hough Transform的应用场景,算法思路,算法步骤以及代码。2.对其应用场景进行更进一步分析,与相似用途的算法(RandSAC)进行比较,分析优缺点。
1.适用场景分析:
拟合问题也可以看成是在参数空间内进行的搜索。在我们遇到拟合问题时,我们需要解答的问题通常是以下几个方面中的一个:
- 已知点集合属于某一个平面(模型),这个模型的参数是多少?
- 点集中可能存在0到多个平面(模型),找到具体有多少模型实例?
- 找到点集中的哪些点对应哪些平面(模型)?
针对每一个问题,考虑到噪音的分布、计算的代价,一般都能找到比较适合的解决方法。Hough Tranform(下文称HT)方法,可以用于解决(但不一定是最适用)全部以上问题。在后面的具体分析中,我们会知道那种场景适合用哪种方法解决。
2.算法思路:
2.1“投票”算法
已知点集\(\{p_1,…,p_n\}\) 中存在平面以及一定数量的噪音,求解最好平面的参数m。拟合问题的解决思路可以用“投票(voting)”来概括:由点 \(p_i\)向其符合的模型\(m_x\)投票,得票者最多的模型胜出成为“最好平面”。从理论上来说,这种方法非常通用,不过,n个点的\(p_i\)与数量不确定的模型之间的组合引发了可穷举性的问题,怎样确定模型的数量?HT解决的就是这个问题。
2.2法向量的转换
平面的方程:\(Ax+By+Cz+D=0\),其中\(\vec v = \begin{bmatrix}A\\B\\C\end{bmatrix}\)为平面的法向量。D为原点\((0,0,0)\)到平面的距离(有符号)。我们可以将法向量\(\vec v\)带入球极坐标系考虑。
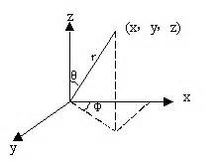
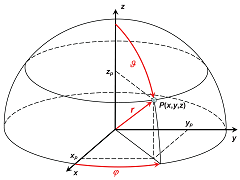
在极坐标系下$$\vec v=\begin{bmatrix}
cos\phi sin\theta \\
sin\phi sin\theta \\
cos\theta \\
\end{bmatrix}$$因为 \(\theta \in [0,2\pi],\phi \in[0,2\pi]\),所以我们可以通过离散\(\theta,\phi\)以及原点到平面的距离\(\rho\)来实现对参数空间的离散化枚举。
2.3累加器
直线方程为 : \( (cos\phi sin\theta) x + (sin\phi sin\theta) y + cos\theta + \rho =0 \),对于点\(p_i\),其针对所有的 \((\theta,\phi)\)带入方程均可求得对应的\(\rho\),因此每个点\(p_i\)都可在参数空间形成了对应参数曲面如下图所示:
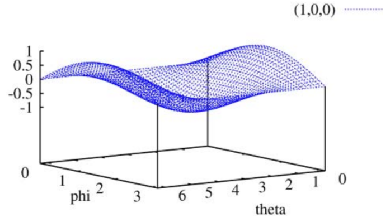
多个点对应的参数曲面会形成多个交点,其中交点最多的参数\((\theta,\phi,\rho)\)即对应的点数最多的平面。如下图所示:
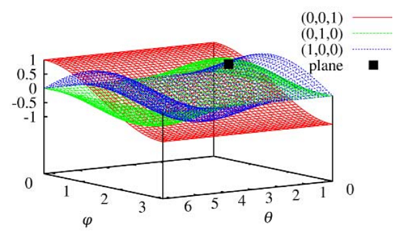
从实现的角度考虑,我们可以构建一个三维的数组,第三维保存符合平面的点的个数,称为累加器。针对每个点\(p_i\),均对其对应的\((\theta,\phi,\rho)\)进行累加。
2.4需要考虑的问题:
以二维HT线检测为例,出于噪声的影响,我们认为的同一条线可能在HT空间上划分为多个\((\theta,\phi,\rho)\) 因而引发其在累加器上的峰值变的模糊(fuzzy),如下图所示。

解决方案是在进行累加值峰值统计时,并不统计每个基本单元的点个数而得到最大值,而是对每个单元的一个邻域进行合并统计,可以帮助解决噪音导致的峰值分散的问题。
第二个问题是,我们认为平面法向量\(v(x,y,z)\)与\((-x,-y,-z)\)是等同的,所以在\(\theta,\phi\)角度的值域上,我们仅选取半球\(\theta\in[0,\pi],\phi\in[0,\pi]\)即可。这样也缩小了计算量。同时,因为法向量的这种对称性,在统计累加器个数时,我们也要认为\(\theta=0\)与\(\theta=\pi\)是毗连的,对\(\phi\)亦然。
3.针对具体应用的改进:
在特定的应用中,我们可能对平面的某些特征进行了更进一步的确定。比如说交通标牌,其法向量通常朝向行车方向,结合HT空间\((\theta,\phi)\)的具体含义,我们可以缩小上述参数的值域范围,因此不但可以排除无关平面的“乱入”,而且极大的加速了算法的效率,减小了不小的一笔计算量。
4.分析以及与类似算法进行对比:
HT算法的优点:
- 所有点都是独立处理的,因此不受离群点的影响。
- 对噪音有一定的鲁棒性(鲁棒性较其他算法好)
- 能够进行多个参数实例(比如说多个不同平面)的识别,是HT的独门绝技。
HT的缺点:
- 计算量极大,计算复杂程度是参数个数的指数倍。
- 非目标要素会造成伪峰值(这一条在应用得到点云平面检测时并未发现)
- 参数离散化的步长比较不好选。
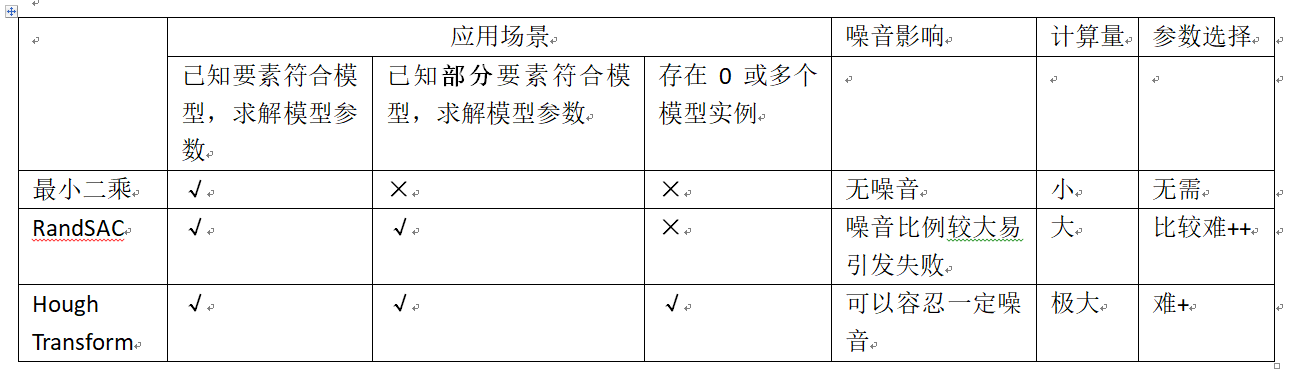
同为“投票”算法并且广泛使用的还有RandSAC算法。在拟合算法中,基本的算法还有最小二乘拟合方法。对这三种方法的适用场景、计算量、噪音影响等进行评估,可以得到下表:
5.参考文献:
- The 3D Hough Transform for Plane Detection in Point Clouds:A Review and a new Accumulator Design
- Feifei Li: Finding lines: from detection to model fittinig
- Fitting: the Hough Transform
- Least Squares. RandSAC.Hough Transform
6.实现代码:
按照参考文献1中的进行实现,文献1中的方位角为\(\theta\),俯仰角为\(\phi\),与本文以及通行的称呼正好相反,请读者在参考时注意区别。
#define PI 3.141592653
void HoughTransform(const std::vector<Point>& input, double& A, double& B, double& C, double& D)
{
int n = input.size();
if (n < 3)
return;
double theta_start=0, theta_end=PI;
double phi_start=0, phi_end=PI;
//double phi_start = 0.25*PI, phi_end = 0.75*PI;
double anglestep=PI/90, disstep=0.1;
boundingbox box;
calcboundbox(input, box);
double d_start = -box.diag() / 2.0, d_end = box.diag() / 2.0;
int thetas = ceil((theta_end - theta_start) / anglestep);
int phis = ceil((phi_end - phi_start) / anglestep);
int dises = ceil( box.diag()/disstep);
int*** cube = new int**[thetas];
for (int i = 0; i < thetas;++i)
{
cube[i] = new int*[phis];
for (int j = 0; j < phis; ++j)
{
cube[i][j] = new int[dises];
memset(cube[i][j], 0, sizeof(int)*dises);
}
}
//cos(theta)sin(phi)X+sin(theta)sin(phi)Y+cos(phi)Z = D
Point ptCenter = box.center();
for (int i = 0; i < n;++i)
{
const Point& ptOrigin = input[i];
Point point = ptOrigin - ptCenter;
double theta = theta_start;
for(int j = 0; j < thetas; ++j)
{
int** row = cube[j];
double phi = phi_start;
for (int k = 0; k < phis; ++k)
{
int* col = row[k];
double sinphi = sin(phi);
double d = cos(theta)*sinphi*point.x + sin(theta)*sinphi*point.y + cos(phi)*point.z;
int d_index = floor((d - d_start) / disstep);
++(col[d_index]);
phi += anglestep;
if (phi > phi_end)
break;
}
theta += anglestep;
if (theta > theta_end)
break;
}
}//all points
int buf = 1;
int maxcount = 0;
int xmax, ymax, zmax;
for (int i = 0; i < thetas;++i)
for (int j = 0; j < phis; ++j)
for (int k = buf; k < dises - buf;++k)
{
int count = 0;
for (int x = i - buf; x <= i + buf; ++x)
for (int y = j - buf; y <= j + buf; ++y)
for (int z = k - buf; z <= k + buf; ++z)
{
count += cube[x<0?x+thetas:x%thetas][y<0?y+phis:y%phis][z];
}
if (count > maxcount)
{
xmax = i;
ymax = j;
zmax = k;
maxcount = count;
}
}
double theta = theta_start + xmax*anglestep;
double phi = phi_start + ymax*anglestep;
double d = d_start + zmax*disstep;
A = cos(theta)*sin(phi);
B = sin(theta)*sin(phi);
C = cos(phi);
D = -d - (A*ptCenter.x + B*ptCenter.y+C*ptCenter.z);
//std::cout << A << " , " << B << " , " << C << " , "<< D << std::endl;
//释放cube
for (int i = 0; i < thetas; ++i)
{
int** row = cube[i];
for (int j = 0; j < phis;++j)
{
int* col = row[j];
delete[] col;
}
delete[] row;
}
delete[] cube;
}
依赖的Point 以及 BoundingBox 的实现如下:
class Point
{
public:
double x, y, z;
Point(double ix,double iy,double iz) :
x(ix), y(iy), z(iz){}
Point operator-(const Point& pt) const
{
return Point(x - pt.x, y - pt.y, z - pt.z);
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
class boundingbox
{
public:
double x_min, x_max;
double y_min, y_max;
double z_min, z_max;
public:
double diag() const
{
double dx = x_max - x_min;
double dy = y_max - y_min;
double dz = z_max - z_min;
return sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz);
}
boundingbox():
x_min(std::numeric_limits<double>::max()),
y_min(std::numeric_limits<double>::max()),
z_min(std::numeric_limits<double>::max()),
x_max(-std::numeric_limits<double>::max()),
y_max(-std::numeric_limits<double>::max()),
z_max(-std::numeric_limits<double>::max())
{}
Point center() const
{
return Point((x_max + x_min) / 2.0,(y_min+y_max) / 2.0, (z_min+z_max) / 2.0);
}
};
void calcboundbox(const std::vector<Point>& input, boundingbox& box)
{
for (int i = 0, n = input.size(); i < n;++i)
{
auto point = input[i];
if (point.x < box.x_min)
box.x_min = point.x;
if (point.y < box.y_min)
box.y_min = point.y;
if (point.z < box.z_min)
box.z_min = point.z;
if (point.x > box.x_max)
box.x_max = point.x;
if (point.y > box.y_max)
box.y_max = point.y;
if (point.z > box.z_max)
box.z_max = point.z;
}
}
